| |
|
|
|
| High binding energy |
|
| The siloxane bonds(-Si-O-Si-) that form the backbone of silicone (dimethyl polysiloxane) are highly stable. At 433 kJ/mol, their binding energy is higher than that of carbon bonds (C-C), at 355 kJ/mol. Thus, compared to common organic polymers, silicone rubbers have higher heat resistance and chemical stability, and provide better electrical insulation. |
| Heat resistance |
|
Flame retardancy |
|
Chemical stability |
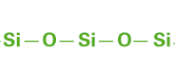 |
| |
| Good weatherability |
|
Radiation resistance |
|
Electrical properties |
|
| |
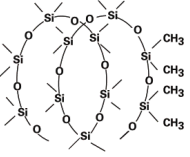
| Intermolecular force is low, and coil formation capacity is high. |
| Silicone molecules are helical and intermolecular force is low, resulting in high elasticity, high compressibility, and excellent resistance to cold temperatures. Furthermore, the methyl groups located on the outside the coil structure can rotate freely. This characteristic gives silicone its distinctive interfacial properties, including water repellency and good releasability. |
Water repellency |
|
Releasability |
 |
|
Cold resistance |
|
Good compression characteristics |
|
| |
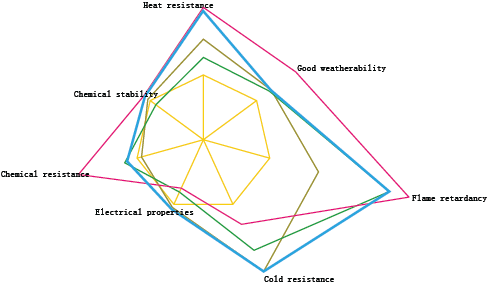
Comparison of properties of various rubbers
using natural rubber as a reference |
 |
 |
|
|