| |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
| 1. Silicone Oil |
|
 |
|
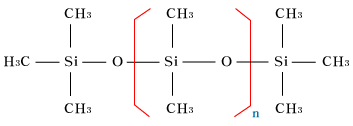
| Polydimethylsiloxane
(PDMS) |
| |
|
| |
|
 |
|
 |
|
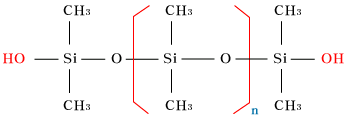
| OH-terminatedpolydimethylsiloxane |
| |
|
| |
|
 |
|
 |
|
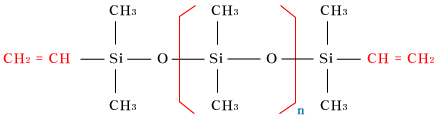
| Vinyl-terminatedpolydimethylsiloxane |
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
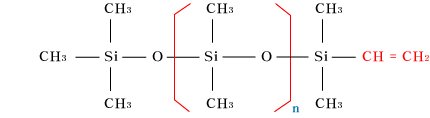
| Silicone oil exists in many denatualized
structures for property improvement and better
quality, but if we take only representative
substances the above molecule is the one.
The frame that forms this molecule is the
siloxane bonding, and as the modecule chain
can move freely among each other becuase each
molecule is independent when they combine
and form a substance, it appears to be fluid,
in other words, liquid. Viscosity varies according
to the degree of polymerization, and in metyl-silicone
oil those with the degree 2 of polymerization
exist from 0.65cSt to hundreds of thousands
of cSt. |
| |
| 2. Silicone Rubber |
|
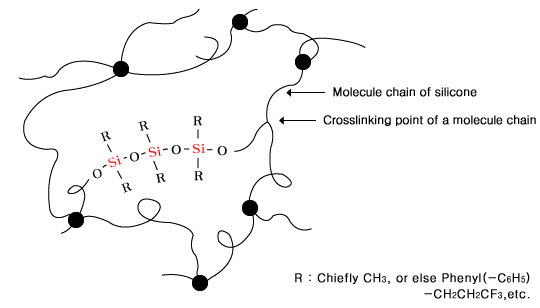 |
| Composed of molecules in net shape, a silicone
rubber appears to be a rubber as it becomes
more random, although less liquid, because
its molecule chains cannot move among each
other unlike silicone oil. |
| |
| 3. Silicone Resin |
|
 |
|
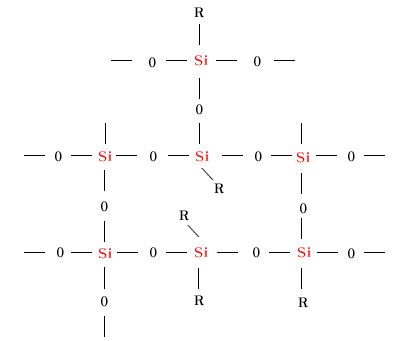
| Silicone rubbers harden as the randomness
of their molecules diminish and their elasticity
decreases as their crosslinking proceeds.
These are called silicone resin when their
crosslinking density is extremely high. Compared
to silicone oil and silicone rubbers that
are mainly composed of 2-functional group
units, silicone resin contains many 3-functional
group units or 4-functional group units. These
resins have the characteristic of forming
hard films and shaped objects, and are used
as varnish for electric insulation, or as
the base resin for weather resistant paints,
or as the base resin of shaping materials,
and for drainage and releasing. |
| |
|